
United States Marshals Service
FY 2025 Performance Budget
President’s Budget
Justice Prisoner and Alien Transportation System
Revolving Fund
March 2024
This page intentionally left blank.
i
Table of Contents
I. Overview ................................................................................................................................1
A. Budget Assumptions ..................................................................................................................... 2
B. Efficiencies, Savings, and Increased Value .................................................................................. 2
C. Budget Summary .......................................................................................................................... 5
D. Revenues and Expenses ................................................................................................................ 5
II. JPATS Performance Challenges..........................................................................................6
A. Invest in Our Workforce: .............................................................................................................. 6
B. Safe and Efficient Prisoner Transport: ......................................................................................... 7
C. Sustainable Infrastructure, Assets and Resources: ....................................................................... 9
III. Performance Tables ............................................................................................................10
1. Performance and Resources Table .............................................................................................. 10
2. Performance, Resources, and Strategies ..................................................................................... 12
IV. JPATS Operating Budget ...................................................................................................13
Chart 1: Changes in the Cost of Operations, FY 2023 – 2025 ......................................................... 13
Chart 2: Sources of New Orders and Revenue, FY 2023 – 2025 ..................................................... 13
Chart 3: Revenues and Expenses ..................................................................................................... 14
V. Exhibits
A. Organizational Chart
B. Summary of Requirements
C. FY 2024 Program Increases / Offsets by Decision Unit (Not Applicable)
D. Resources by DOJ Strategic Goals and Strategic Objective
E. Justification for Technical and Base Adjustments (Not Applicable)
F. Crosswalk of 2023 Availability
G. Crosswalk of 2024 Availability
H. Summary of Reimbursable Resources
I. Detail of Permanent Positions by Category
J. Financial Analysis of Program Changes (Not Applicable)
K. Summary of Requirements by Object Class
N. Schedule of Aircraft
Q. Awards
ii
This page intentionally left blank.
1
I. Overview
The Justice Prisoner and Alien Transportation System (JPATS) coordinates and executes
prisoner and detainee movements safely, securely, and humanely in a timely and economical
manner. JPATS operates as a revolving fund with total operating costs reimbursed by its
customer agencies, the U.S. Marshals Service (USMS) and the Federal Bureau of Prisons (BOP).
JPATS also transports prisoners from other Federal agencies such as the Department of Defense
as well as state and local agencies on a reimbursable, space-available basis.
Using USMS and BOP projected prisoner movement requirements, JPATS develops total
projected costs associated with air transportation. JPATS uses OMB Circular A-126 guidelines
to identify fixed and variable cost categories and applies activity-based costing to develop flight
hour rates. JPATS bills its customers based on the number of flight hours and the number of
seats used to move prisoners/detainees.
As a revolving fund, JPATS operates with numerous benefits, including but not limited to:
• the no-year account provides a consistent funding stream that mitigates risks of funding
shortfalls when unanticipated customer program changes or cost variances occur;
• the concept of full-cost recovery achieves program goals for transparency, equitable
distribution of costs, and adherence to industry best practices;
• the revolving fund allows for multi-year funding and leasing authority for capital
acquisitions; and
• the authority to retain proceeds from disposal of aircraft, support equipment, and parts
encourages good stewardship and disciplined asset management.
The JPATS revolving fund stabilizes costs for customer agencies because it can absorb
fluctuations in operating expenses such as fuel and aircraft maintenance on a short-term basis.
JPATS sets aside funds to replace aging aircraft, major aircraft parts, aircraft Ground Support
Equipment (GSE), and hangar/facility improvements over time. JPATS also plans procurement
of equipment, maintenance, and operational facility lease agreements when needed.
JPATS is committed to ensuring each scheduled mission is properly staffed with a well-trained,
professional crew. Each mission includes qualified pilots and aircraft maintenance personnel to
safely operate the aircraft. Experienced law enforcement and security officers ensure crew and
airlift site safety and the safe, secure transfer of prisoners. Each flight is also staffed by a
certified medical specialist who validates required screenings and medical records ensuring all
prisoners are medically stable and fit to fly.
JPATS continually strives to improve the quality of prisoner movement services, optimize the
transportation network, and produce efficiencies for the customer.

2
A. Budget Assumptions
Key assumptions for this budget formulation include:
• Costs associated with operating and maintaining complex, advanced aircraft continue to
increase. The FY 2025 Budget reflects the planned cyclical replacement of JPATS-
owned B-737-400 “Classic Series” aircraft. Classic series asset replacement will
continue as these aging aircraft are replaced with Next Generation (Next Gen) 737s from
the aviation industry. Next Gen aircraft offer JPATS employees, customers, and
stakeholders greater capabilities and more value in the form of reliability, fuel efficiency,
and operational safety. Next Gen aircraft provide improved technologies and greater
capabilities, but at increased transportation unit costs. JPATS completed Cyclical
Replacement Phase I (of III) in FY 2022 with the purchase of a B737-800 and sold the
replaced legacy B737-400 in FY 2023. JPATS anticipates completion of Cyclical
Replacement Phase II in FY 2024. JPATS will start actively working toward
implementation of Phase III as soon as Phase II is completed.
• The price per gallon of jet fuel continues to fluctuate. Less expensive contract fuel is
purchased wherever possible but is not always available at mission critical airlift stops.
• Ownership of large aircraft, including a contingency aircraft, ensures greater availability
for missions, affords surge capability, and is more cost-effective than leasing aircraft.
B. Efficiencies, Savings, and Increased Value
JPATS continually examines its operational areas to provide reliable and safe, quality services
while seeking to increase efficiencies and generate savings for the customer agencies.
JPATS Efficiencies
JPATS continues to lead optimization efforts to improve performance and increase efficiency.
The data and analysis made possible by the JPATS Management Information System (JMIS) are
central to current and planned program initiatives. More accurate and timely data is now
available to help management analyze program areas, and JPATS is using performance data to
identify potential problems, create solutions, and drive program improvements.
JPATS Savings
The JPATS Large Aircraft Contingency initiative creates increased operational stability and
sustained program savings for its partners as expected. Maintaining three JPATS-owned 737
aircraft, in support of Oklahoma City-based operations, ensures optimal availability by providing
a contingency aircraft for use when primary aircraft are undergoing maintenance or when surge
missions are required. With the additional 737, JPATS sustained a 99 percent aircraft
availability rate in Q4 FY 2023, allowing for an additional 53 missions to occur without the need
for procuring charters or flying extra missions using the contingency aircraft. JPATS completed
233,825 prisoner movements through Q4 in FY 2023. The Federal Prisoner Detention
appropriation would have incurred an estimated $1,600,000 in additional housing costs if the
contingency aircraft was not in place. This is based on an average detention cost of $107.63 per

3
day, while detainees await transfer to the BOP. Ownership of the 737-800 and 737-700 aircraft
have proven to provide JPATS greater operational flexibility, fewer logistical concerns due to a
common platform for all large aircraft, and a reduced security risk. With this additional asset,
JPATS is now able to readily conduct on-demand flights for its partners to overseas locations
such as the District of Hawaii without external resources. JPATS conducted its first mission of
the newly purchased 737-800 in February 2022, and regularly conducts flights as required by
JPATS’ customers.
JPATS Increased Value
JPATS provides value and meets customer expectations by continually reviewing program
performance metrics and accommodating customer requirements. JPATS monitors weekly,
monthly, and quarterly performance, and provides reports to the USMS Director and the JPATS
Executive Committee through the JPATS Working Group. JPATS continues to seek solutions
that add value to the program. For example, JPATS is working toward executing Phase II of the
Cyclical Replacement plan. The solicitation to acquire another Next Gen aircraft was posted in
late FY 2023 and awarded in the first quarter of FY 2024. The delivery of the new aircraft is
expected in early second quarter of FY 2024.
For the contract period of FY 2019 through FY 2023, JPATS transitioned its aircraft
maintenance provider from the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) Universal Service
Agreement to an industry leading commercial aircraft maintenance vendor. This transition
increased value to JPATS customers by reducing maintenance costs and minimizing aircraft
downtime. Given this success, JPATS re-competed the contract and the same commercial
vendor won the contract for the period FY 2024 through FY 2028. The vendor is a proven
experienced maintainer that provides exceptional maintenance and repair capabilities, quality
aircraft parts service, and contributed to sustaining a 99 percent Boeing 737 mission reliability
rate in FY 2023.
Based upon the Executive Order 14006’s requirement to eliminate the use of private prison
facilities, BOP and the USMS deactivated many private facilities across the United States from
FY 2021 through FY 2023. With Nevada Southern Detention Facility near Las Vegas planned
deactivation and no other housing options available for the JPATS Las Vegas hub, JPATS
assessed future stationing options for its Boeing 737-700 in Las Vegas, Nevada. Based upon an
analysis of national prisoner demands, the Executive Order, and notification of BOP mission
changes at United States Penitentiary (USP) Leavenworth, JPATS recommended a relocation to
Kansas City, Missouri.
In September of 2023, JPATS relocated its Las Vegas aircraft to Kansas City. At the same time,
JPATS completed a Transfer of Function for the 11 positions based in Las Vegas to the Kansas City
site and closed out the General Services Administration (GSA) lease for the operational site at the
Harry Reid International Airport in Las Vegas. Currently, hub beds in USP Leavenworth have not
become available to JPATS. However, JPATS worked with the USMS Prisoner Operations
Division to obtain alternative prisoner housing. This location, along with the primary Oklahoma
City operational site, will optimize route effectiveness and provide higher seat utilization in the
national prisoner transportation network. Stationing aircraft closer to USMS detainee housing and
4
BOP facilities reduces the need for low-volume flights that increase operating costs. This will also
lower the overall in-transit time by allowing designated prisoners to arrive at their final BOP
destinations sooner. Consolidating the Las Vegas JPATS location into the larger Kansas City
headquarters will reduce the JPATS footprint from three sites to two and drive further operational
efficiencies.

5
C. Budget Summary
JPATS Revolving Fund program estimates for Obligation Authority (OA) and Personnel Data
are based upon customers’ projected requirements and estimated carry forward authority.
Financial Operations, FY 2023 – 2025
($ in thousands)
FY 2023
Actual
FY 2024
Estimate
FY 2025
Estimate
Operating
59,497
78,617
79,974
Less Depreciation
(2,518)
(7,289)
(7,197)
Operating Authority
56,979
71,328
72,777
Unobligated Balance End-of-Year*
58,527
67,816
75,013
Total Authority
115,506
139,144
147,790
Civilian Positions
123
123
123
Civilian End Strength
98
113
114
Personal Contract Guards
104
135
135
Average GE Salary
$104,449
$106,652
$110,455
Average SES Salary**
$155,037
$216,016
$216,830
* From SF-133, “Report on Budget Execution and Budgetary Resources,” dated November 30, 2023.
Unobligated balance is updated from the FY 2025 President’s Budget Appendix to correct a USMS error.
** SES position was filled by Acting Assistant Director during FY 2023.
D. Revenues and Expenses
Estimated Accumulated Operation Results (AOR) for FY 2023, FY 2024, and FY 2025 are
shown below. The Revenue and Expenses chart on page 14 provides corollary details.
Revenues and Expenses, FY 2023 – 2025
($ in thousands)
FY 2023
Actual
FY 2024
Estimate
FY 2025
Estimate
Revenue* 63,481 78,617 79,974
Cost Of Operations (includes depreciation) (53,592) (78,617) (79,974)
Operating Results 9,889
0
0
Non-Operating Adjustment – Other (4,764) 0 0
Net Operating Results (NOR) 5,125 0 0
Prior Year AOR 66,617 71,742 71,742
AOR Adjustments 0 0 0
Net Accumulated Operating Results (AOR) 71,742 71,742 71,742
*
FY 2024 and FY 2025 revenue estimates are updated from the FY 2025 President’s Budget Appendix to correct
a USMS error.
6
II. JPATS Performance Challenges
Transporting Federal Prisoners in Support of the American Justice System
Challenge: JPATS must transport prisoners safely, timely, and economically within limited
resources to provide the best value to its customers. JPATS must look for innovative solutions to
create greater efficiency and sustain optimum program performance within the current
transportation infrastructure.
A. Invest in Our Workforce:
Invest in the development of our workforce to ensure a highly skilled, cohesive, and high-
performing team culture.
Strategy: Core Values: Incorporate our core values of integrity, professionalism,
teamwork, and service into everything we do.
JPATS completed improvements to its security program to increase its protective posture, raise
threat awareness, and reduce risk. Starting with operational security, JPATS continues to ensure
professional and competent airlift perimeter and hangar security procedures by committing to
monthly, quarterly, and annual weapons and tactics training. Additionally, JPATS procured
improved tactical gear, radios, tasers, and firearms to align with USMS and DOJ policies.
JPATS continues to improve intelligence capabilities by providing analysts with additional
database access allowing for more robust risk assessments. JPATS analysts also enhance their
capabilities through partnership with local, regional, and national law enforcement intelligence
centers to provide operational personnel the current risk data. These enhancements heighten
threat awareness while providing an enhanced security posture, thus improving officer, crew, and
public safety.
During FY 2023 and into FY 2024, JPATS’ operational staff continued to experience numerous
vacancies, due to retirements, resignations, and promotions. JPATS therefore sought to hire
operational personnel with the experience and skill sets necessary for smooth integration and
minimal impact to the mission. During the first quarter of FY 2024, JPATS identified,
interviewed, and selected five diverse and highly qualified individuals for the positions of
Aviation Enforcement Officer (three positions) and Paramedic (two positions). On arrival to
JPATS, new Aviation Enforcement Officers (AEO) complete the USMS Training Division-
approved AEO induction program and a rigorous Enforcement Officer Training Program
(EOTP) curriculum at the Federal Law Enforcement Training Center. This program reduces risk
and standardizes weapons, tactics, and aviation safety training for JPATS operational personnel,
enabling JPATS to sustain its superior aviation safety and enforcement posture. New JPATS
Paramedics will complete a meticulous JPATS internal training program, where they will be
instructed on medical protocols, equipment, procedures, and reviews of previous medical
emergencies.
7
In the first quarter of FY 2024, JPATS also internally promoted five experienced AEOs to fill
vacant AEO leadership positions due to retirements. These promotions created open positions
for new entry-level AEO positions that will now need to be filled to complete JPATS operational
staffing needs.
In FY 2024, JPATS continued coordinating hangar security improvements through the USMS
Judicial Security Division (JSD), Office of Security Systems (OSS). JPATS and JSD are
working together in a joint effort in the design, procurement, and installation of a motor vehicle
access-controlled gate. This security enhancement will provide for greater security at the JPATS
hangar to protect employees and government assets from adversaries. Additionally, this access-
controlled gate will improve vehicle traffic and deliveries at the hangar.
B. Safe and Efficient Prisoner Transport:
Maximize safety and efficiencies in prisoner transport through excellence in law
enforcement, aviation, and business environments.
Strategy: Customer Service and Engagement – Improve our services to meet evolving
customer needs.
In concert with USMS and BOP, JPATS continues to implement a project to automate processes
and documents required for prisoner movement into an electronic Movement Packet (MPAC)
system. A paper prisoner movement packet is currently required to accompany the
prisoner. The new system, which uses secure technology, facilitates the transfer of prisoners
from one transport officer or facility to another across DOJ partners by incorporating electronic
movement requests from data provided by USMS and BOP systems. MPAC will increase
efficiency and accuracy by enabling facilities and transport staff to review the documents prior to
movement on a desktop, laptop, or mobile device. Most notably, the review prior to or “just in
time” at airlift sites will reduce errors produced from rekeying data across systems and eliminate
prisoner transfer denials that arise from missing paperwork.
In Phase 1, the USMS completed the design for the electronic MPAC. In Phase 2, the agency
successfully deployed the electronic MPAC to USMS districts, USMS intergovernmental (IGA)
facilities, and BOP institutions. As this application becomes fully utilized by the USMS and
BOP, it will greatly reduce the amount of paper and workload of staff required to manually print,
copy, and assemble require paperwork for every prisoner movement. Additionally, it will
streamline the exchange of custody during transport and eliminate the verification of paperwork
during the process. Prisoner documents are now automatically retrieved from Capture and
BOP's Electronic Inmate's Central File (EICF) and centrally accessed in MPAC by USMS
districts, USMS IGA facilities, and BOP institutions involved in prisoner transport. A notable
feature of the application is the use of biometric identification and verification to validate
prisoner movements.
8
Strategy: Administration/Scheduling/Communications – Optimize the management of air
and ground movements.
JPATS’ goal is to automate 80% of planned prisoner movements requests. Automated planning
without human intervention, allows transportation specialists to focus on high priority, complex
prisoner transportation scheduling. For over 10 years JPATS utilized a commercial off the shelf
(COTS) shipping software product to perform automated planning. The current system has
successfully performed prisoner movement planning, but the configuration of the software is
labor intensive and costly to maintain to fulfill JPATS requirements. A customized solution is
currently in development that will utilize historic movement data and business intelligence to
provide more accurate prisoner movement planning and require much less maintenance with a
lower cost of ownership. JPATS expects this new product will be deployed to production and
replace the current COTS product by the end of the second quarter in FY 2024.
Strategy: Aviation Safety - Ensure a predictive zero-incident aviation safety program.
JPATS leverages the extensive aviation professional experience of its staff with established
practices and proven technologies to maximize safety, reliably perform to standards, and
minimize risks. The organization continues to enhance its comprehensive aviation Safety
Management System. JPATS has been recognized by the Federal community for its program
that defines and documents operations and adheres to the International Standards-Business
Aviation Organization (IS-BAO) and Federal Aviation Interagency Committee for Aviation
Policy best practices. JPATS continues to maintain an IS-BAO Stage III Certification, which is
considered the gold standard for safe and effective operations in Federal Aviation and
International Commercial Aviation organizations. JPATS’ most recent IS-BAO audit occurred
in November 2022, which is a requirement of the International Civil Aviation Organization for
aviation operations outside the United States. In FY 2023 like prior years, JPATS achieved its
mission with zero accidents or incidents.
In FY 2023, JPATS aviation managers continued to expand aviation training methods and
ensured documentation complied with FAA standards. Their review identified best practices for
maintenance and scheduling personnel, resulting in development of a formal training program
within the aviation department. JPATS continues to transform aviation support functions and
train its personnel for optimal aviation operations. JPATS leveraged local airport support and
cross training by being a major player in an airport accident exercise using JPATS’ aircraft and
staff at the Oklahoma City airport. Simultaneously, JPATS continues to explore new
technologies such as predictive analysis tools, enabling the organization to foresee and mitigate
risks of potential incidents or accidents. Due to in-house safety expertise, JPATS is often invited
to send auditors to participate in other Federal agencies’ IS-BAO or other aviation safety audits.
9
Strategy: Intelligence Research Specialist and Intelligence - Ensure known and emerging
threats to security and aviation are effectively countered.
JPATS continues to improve its capability to produce quality and timely intelligence on
prisoners and operational sites to maintain safe and secure missions. JPATS maintains an
Intelligence Research Specialist program that ties into intelligence assets across the USMS, BOP,
and other Federal agencies to develop and share prisoner attributes and threat information
relevant to prisoner operations and transportation. Throughout FY 2023, daily actionable
intelligence reports continue to mitigate risks associated with potential threats during
transportation operations. The program incorporated additional training and access to additional
national databases, furthering its ability to develop and share prisoner attributes and threat
information. JPATS continues to increase the acquisition of prisoner attribute data using JMIS
and Capture and to develop daily intelligence products for its crews to access through mobile
devices. These capabilities and ease of this technology allows operational personnel to quickly
address, manage, and mitigate emerging intelligence issues to ensure the safe transportation of
prisoner from both ground and air.
C. Sustainable Infrastructure, Assets and Resources:
Maintain a sustainable infrastructure ensuring available and reliable assets to support service
delivery and customer requirements.
Strategy: Business Intelligence and Reporting – Leverage technology to optimize business
intelligence and reporting.
In FY 2023, JPATS began using business intelligence tools to enhance its system development
cycle by allowing easier comparison between the performance of new and existing prisoner
movement planning systems. This allows for more quickly and precisely identifying areas of
opportunity to get the most out of the development lifecycle. Additionally, JPATS began
developing basic machine learning tools to enhance the prisoner movement planning and
scheduling process. Expected to come online in FY 2024, the new planning and scheduling
system will greatly improve prisoner planning performance by moving prisoners out of paid
housing quicker and getting them to their destination expeditiously saving time and money.
10
III. Performance Tables
1. Performance and Resources Table
PERFORMANCE AND RESOURCES TABLE
Decision Unit: Justice Prisoner and Alien Transportation System
RESOURCES ($ in thousands)
Target
Actual
Projected
Changes
Requested (Total)
FY 2023 FY 2023 FY 2024
Current Services
Adjustments and FY
2025
Program Changes
FY 2025
Request
Total Costs and FTE
(reimbursable FTE are included, but reimbursable costs are bracketed and
not included in the total)
FTE
$000
FTE
$000
FTE
$000
FTE
$000
FTE
$000
113 $68,739 98 $56,979 113 $71,328 1 $1,449 114 $72,777
Strategic
Objective
Type Performance FY 2023 FY 2023 FY 2024
Current Services
Adjustments and FY
2025 Program Changes
FY 2025
Request
Program
Activity
Prisoner Movement
FTE Amount FTE Amount
FTE Amount
FTE Amount FTE Amount
113 $68,739 98 $56,979
113 $71,328 1 $1,449 114 $72,777
5.2
Perf. Measure:
Output Workload
Number of requests for air and
ground transportation of prisoners
98,200 90,376 92,600 2,700 95,300
5.2
Perf. Measure:
Output Unit Cost
Transportation unit cost $1,900
$1,931 $1,750 $200 $1,950
11
PERFORMANCE MEASURE TABLE
Decision Unit: Justice Prisoner and Alien Transportation System
Strategic
Objective
Performance Measure
FY 2023 FY 2024 FY 2025 FY 2026
Target Actual Target Target Target
5.2 Workload
Number of requests for air and ground
transportation of prisoners
98,200
90,376 92,600 95,300 98,500
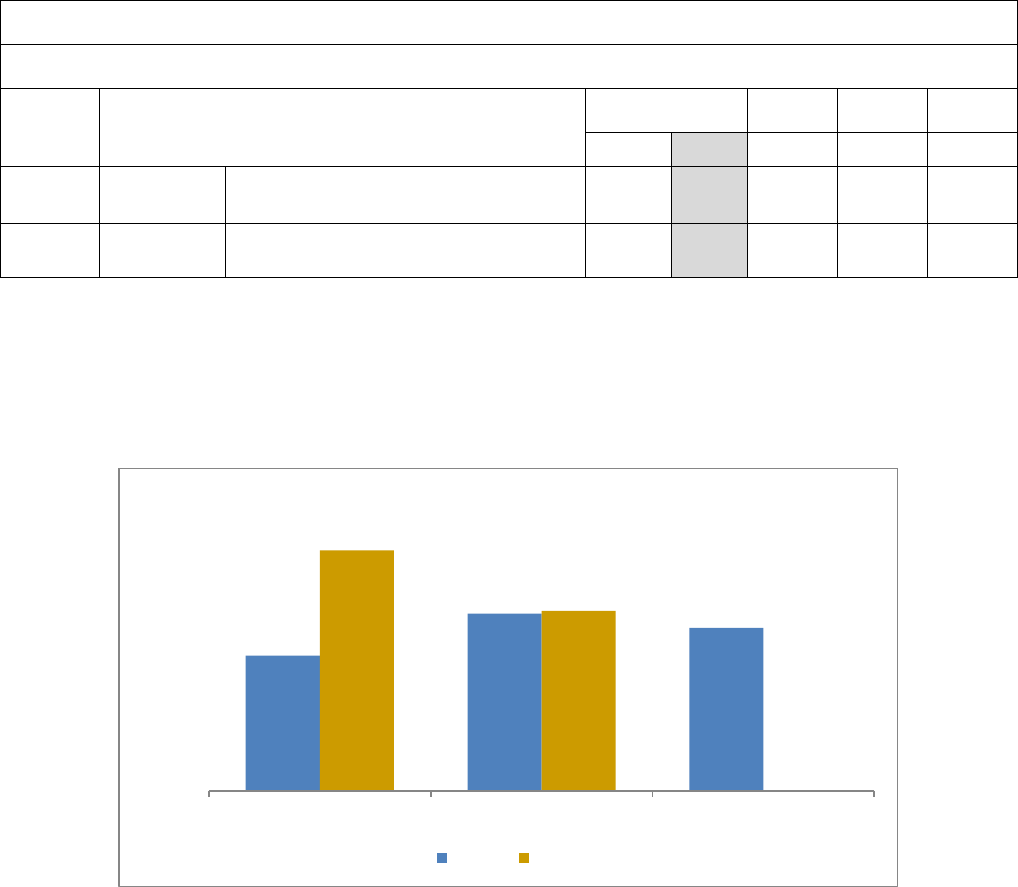
5.2 Output Transportation unit cost* $1,900 $1,931 $1,750 $1,950 $2,000
* The FY 2025 target was updated from $1,800 per rate-based prisoner (as reported on the FY 2024 President’s Budget) to $1,950. Target
Workload estimates for FY 2023, FY 2024, and FY 2025 were also reduced compared to the previously reported FY 2023 President’s
Budget projections. Historical transportation unit cost is depicted in the graph below.
Transportation Unit Cost by Fiscal Year
$1,450
$1,900
$1,750
$2,580
$1,931
$-
$0
$500
$1,000
$1,500
$2,000
$2,500
$3,000
FY 2022 FY 2023 FY 2024
Target Actual
12
2. Performance, Resources, and Strategies
a. Performance Plan and Report for Outcomes
JPATS routinely builds on partnerships with the USMS and BOP. JPATS’ goals and
objectives are designed to maintain financial and operational responsibilities for transporting
prisoners, conduct effective daily operations, and promote problem resolution and process
improvement at the national level. JPATS leverages technology, participates with the USMS
in implementing Capture, and partners with the BOP to integrate and advance data-sharing
solutions focused on providing more efficient management decision data and reporting
capabilities across the agencies.
JPATS assesses current and potential airlift sites and routes to validate site and route
selection and to develop a standardized process to initiate and complete airlift site
assessments. This process ensures that JPATS regularly revalidates aviation, security, and
business considerations, but also provides its partners a mechanism to request changes that
emphasizes transparency, information sharing, and documentation.
b. Strategies to Accomplish Outcomes
Efficient scheduling and execution of prisoner transfers are the most effective ways JPATS
can reduce bed-space expenses. JPATS achieves this by using automation to create dynamic
scheduling that is responsive to facility capacity constraints and to replace paper-based
processes. JPATS automation reduces errors and ensures better scheduling information.
These benefits reduce refusals during transport and facility exchanges, which subsequently
results in fewer delays and lower contracted bed-space costs.
JPATS supports transportation services through mobile technology. The use of mobile
devices serves to expedite operations, improve data collection and reporting, and reduce risk.
Risk reduction activities with mobile technology components include the provision of
electronic prisoner manifests with prisoner photos and key information to aviation
enforcement officers; real-time weather updates and airport information to JPATS
dispatchers and pilots; and in-flight prisoner medical information to mission paramedics for
communication to medical practitioners during immediate care.
To provide safe, secure, and economical prisoner transportation, JPATS focuses on the safety
of its staff. JPATS applies a two-pronged strategy to maintain its safety culture. First,
JPATS continuously assesses staffing requirements and utilizes employee scheduling
alternatives to ensure personnel with special skills are available on each mission.
Additionally, JPATS consistently conducts specialized aviation law enforcement training for
both employees and contractors to enhance officer safety and standardization.

13
IV. JPATS Operating Budget
Due to timing of the budget submission, Estimated Revenue amounts shown in the charts below
deviate from amounts shown in the Budget Appendix.
Chart 1: Changes in the Cost of Operations, FY 2023 – 2025
($ in thousands)
Chart 2: Sources of New Orders and Revenue, FY 2023 – 2025
($ in thousands)
New Orders
FY
2023
FY
2024
FY
2025
a. Operating Orders From Customers
USMS $35,695 $50,633 $51,929
BOP $27,420 $27,984 $28,045
Other 315 0 0
b. Non-Operating Orders
USMS 0 0 0
BOP 0 0 0
Other – Proceeds from Sale of Aircraft 1,920
Total Orders from Customers $65,350 $78,617 $79,974
* FY 2024 and FY 2025 revenue estimates updated and differ from the FY 2025 Budget Appendix.
FY 2023 Actual*
$65,350
FY 2024 Estimate*
$78,617
Pricing Adjustments:
Pricing Adjustments:
Aircraft Fuel
2,048
Aircraft Fuel
882
Aircraft Maintenance
8,679
Aircraft Maintenance
(988)
Aircraft Leases
1,047
Aircraft Leases
201
Civilian Labor
3,552
Civilian Labor
288
Guards, Contract Services
1,180
Guards, Contract Services
2,479
Employee Training
621
Aircraft Ground Support
(149)
Medical Expenses
261
Facilities Expense
(241)
Administrative Expenses
1,084
Administrative Expenses
90
Depreciation
Depreciation
(93)
Equipment
1,179
Equipment
(884)
Other
Loss on sale of aircraft
(1,620)
(4,764)
Other
(228)
Subtotal
$13,267
Subtotal
$1,357
FY 2024 Estimate* $78,617
FY 2025 Estimate* $79,974
* Includes depreciation.

14
Chart 3: Revenues and Expenses
Revenues and Expenses, FY 2023 – 2025
($ in thousands)
Description FY 2023 FY 2024 F
Y 2025
REVENUE (Actual) (Estimate) (Estimate)
Operations
$63,481 $78,617 $79,974
Other Income
0 0
Total Revenue
63,481 78,617 79,974
EXP ENS ES
Aircraft Operating Expenses
Aircraft Fuel
11,977 14,025 14,907
Aircraft Maintenance
8,316 16,995 16,007
Aircraft Leases
3,692 4,739 4,940
Aircraft Operating Expenses Total
23,985 35,759 35,854
Labor Related Expenses
Civilian Labor
15,277 18,829 19,117
Employee Training
174 795 753
Guards, Contract Services
3,774 4,954 7,432
Labor Related Expenses Total
19,225 24,578 27,302
Mission Support Expenses
Contract Crew
- - -
Aircraft Ground Support Expenses
366 527 378
Navigation Data, Tech Periodicals
357 395 379
Medical Expense
231 492 337
Mission Travel
290 495 498
Mis s ion Support Expens es Total
1,244 1,909 1,592
Non-Mission Support Expenses
Facilities Expenses
2,298 2,311 2,070
Admin & Support Expenses (incl. IGAs)
3,321 4,405 4,495
Equipment Purchase/Rental
634 1,813 929
Non-Mission Travel
209 553 535
Other Expenses
158 0 0
Non-Mis s ion Support Exp Total
6,620 9,082 8,029
Total Expens es
51,074 71,328 72,777
Operating Results
12,407 7,289 7,197
Depreciation
(2,518) (7,289) (7,197)
Net Operating Results
9,889 0 0
Net Loss on Sale of Aircraft/Equipment
(4,764) 0 0
Prior Year Accumulated Operating Results
66,617 $71,742 71,742
Accum. Operating Result Adjustments
0 0 0
Net Accumulated Operating Results
$71,742 $71,742 $71,742
